Literature survey and benchmark for sparse polynomial chaos expansions
Principal investigators: N. Lüthen
Description
To explore the influence of input uncertainties on the output of complex computer models by Monte Carlo simulation, many model evaluations are needed. A popular technique for reducing the resulting computational cost is surrogate modelling: first, a proxy of the original computational model is constructed from few model evaluations. Then this cheap-to-evaluate surrogate model is used for the uncertainty analysis.
A particularly popular and powerful surrogate modelling technique is Polynomial Chaos Expansions (PCE), and specifically sparse PCE, which express the computational model sparsely in a basis of orthogonal polynomials. Established only 10 years ago, the literature on sparse PCE has been growing considerably in the recent years. Many promising methods have been proposed, but it was not clear which of the many methods would be most suitable for a given problem.
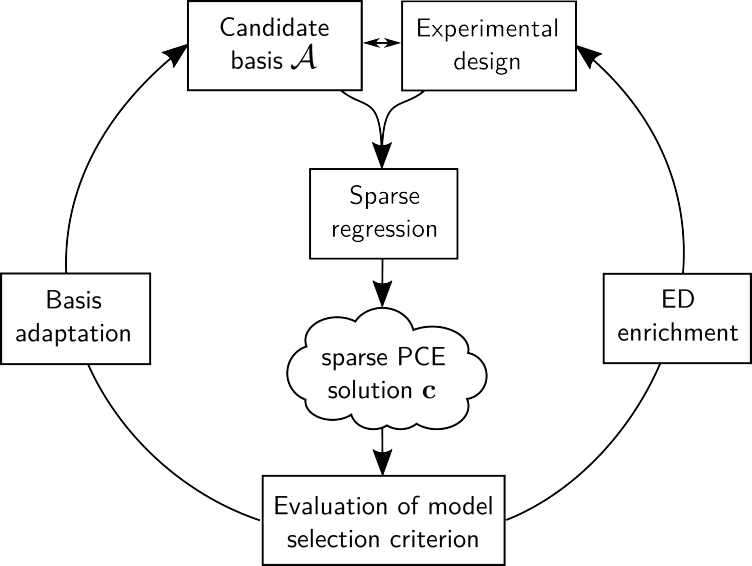
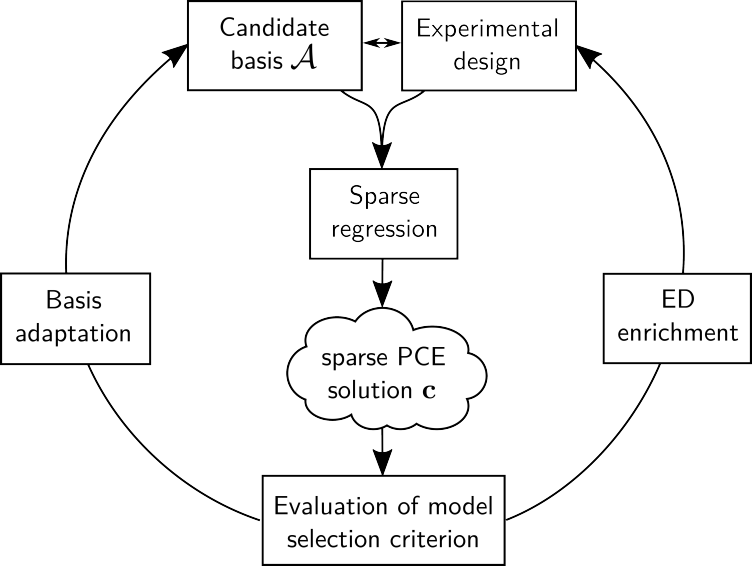
In this project, we conducted a literature survey and several benchmarks for sparse PCE (external page Lüthen et al., 2021 and external page 2022). We organized the methods into a common framework and compared the most promising methods on a set of 11 benchmark models representative of real-world engineering problems. While no method consistently outperforms all others, we were able to extract recommendations on which method to use in different situations.
Um durch Monte-Carlo-Simulation herauszufinden, welchen Einfluss Ungewissheiten in den Inputparametern auf den Output komplexer Computermodelle haben, werden viele Modellauswertungen benötigt. Eine beliebte Methode zur Verringerung der Rechenkosten ist die Ersatzmodellierung: Zunächst wird mithilfe weniger Modellauswertungen eine Annäherung an das Computermodell erstellt. Dieses kostengünstigere Ersatzmodell wird dann anstelle des ursprünglichen Modells für die Ungewissheitsanalyse verwendet.
Eine besonders beliebte und leistungsfähige Ersatzmodellierungsmethode ist polynomial chaos expansions (PCE), insbesondere dünnbesetzte PCE, welche das Computermodell mithilfe weniger Elemente einer orthogonalen Polynombasis annähert. Obwohl diese Methode erst vor 10 Jahren entwickelt wurde, gibt es bereits eine beträchtliche Anzahl Publikationen zu diesem Thema. Dabei ist oft nicht klar, welche der vorgeschlagenen Berechnungsmethoden sich am besten für ein gegebenes Problem eignen.
In diesem Projekt erstellten wir eine Literaturübersicht für dünnbesetzte PCE, kategorisierten die Methoden mithilfe eines Flussdiagramms (siehe Abbildung) und führten mehrere Vergleichstests auf 11 beispielhaften Computermodellen durch (external page Lüthen et al., 2021 und external page 2022). Obwohl keine Berechnungsmethode durchgängig besser abschneidet als alle anderen, konnten wir Empfehlungen ableiten, in welchen Situationen welche Methode verwendet werden sollte.