Stochastic spectral embedding
Principal investigators: P.-R. Wagner
Description
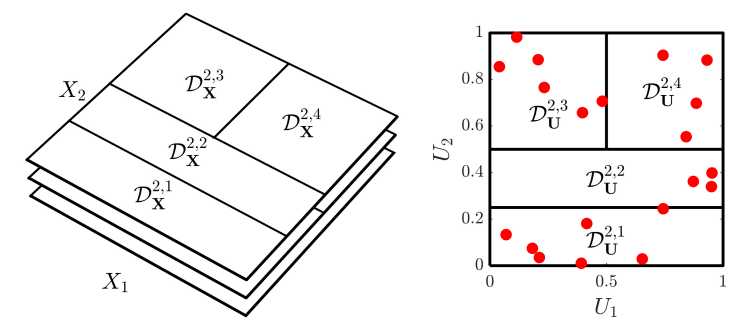
Most methods of uncertainty quantification (UQ) require repeated evaluations of investigated computational models. The increased computation-al cost of those models has spurred the development of so-called non-intrusive surrogate models. These models are trained on samples of the model inputs and their corresponding model responses. They can be used in UQ applications as cheap-to-evaluate replacements of the original model, resulting in a dramatic overall reduction of required computational resources.
Nowadays, there exists a wide array of powerful surrogate modelling techniques with different application-specific strengths (polynomial chaos expansions, Kriging, low-rank approximation, etc.), but models with complex local characteristics remain challenging. In this project, we propose a novel type of surrogate model that utilizes the predictive power of spectral expansion techniques. This technique called stochastic spectral embedding (SSE, external page [1]), sequentially constructs spectral expansions in orthogonal subdomains of decreasing size in the input space, based on the residual of previously constructed expansions. The SSE surrogate can efficiently approximate models with local characteristics that are challenging for other techniques.
Additionally, the local spectral expansion allows post-processing of the SSE expansion coefficients to analytically compute Sobol’ sensi-tivity indices. The flexibility of the proposed approach is subject to ongoing research to extend this framework for other UQ methods such as active learning in reliability.
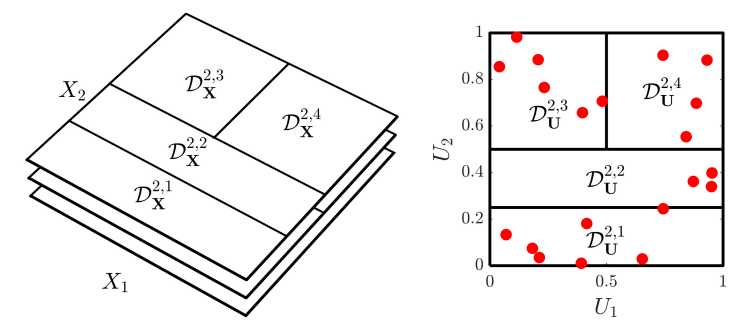
Die meisten Methoden zur Ungewissheitsquantifizierung (UQ) beruhen auf wiederholten Auswertungen der untersuchten Computermodelle. Die hohen Berechnungskosten dieser Modelle haben zur Entwicklung sogenannter nicht-intrusiver Ersatzmodelle geführt. Diese Modelle werden anhand von Stichproben der Modelleingaben und ihrer entsprechenden Modellantworten erstellt. Sie können in UQ-Anwendungen als günstiger Ersatz des ursprünglichen Modells verwendet werden, was insgesamt zu einer drastischen Reduktion der erforderlichen Rechenressourcen führt.
Heutzutage gibt es eine breite Palette leistungsfähiger Ersatzmodellierungstechniken mit unterschiedlichen anwendungsspezifischen Stärken (polynomial chaos expansions, Kriging, low-rank approximations, usw.), Modelle mit komplexem lokalen Verhalten sind jedoch nach wie vor herausfordernd. In diesem Projekt schlagen wir ein neuartiges Ersatzmodell vor, das die Vorhersagekraft spektraler Expansionstechniken nutzt. Diese als stochastische spektrale Einbettung (SSE, external page [1]) bezeichnete Technik konstruiert nacheinander spektrale Expansionen in orthogonalen Subdomänen mit abnehmender Größe, basierend auf den Residuen zuvor konstruierter Expansionen. Der SSE-Ersatz approximiert effizient Modelle mit lokalem Verhalten, die für andere Techniken eine Herausforderung darstellen.
Darüber hinaus ermöglicht die lokale spektrale Expansion die Nachbearbeitung der SSE-Expansionskoeffizienten, um die Sobol-Sensitivitätsindizes analytisch zu berechnen. Die Flexibilität des vorgeschlagenen Ansatzes wird zurzeit erforscht, um dieses Verfahren für andere UQ-Methoden wie aktives Lernen bei Zuverlässigkeitsanalysen zu erweitern.